pb 7
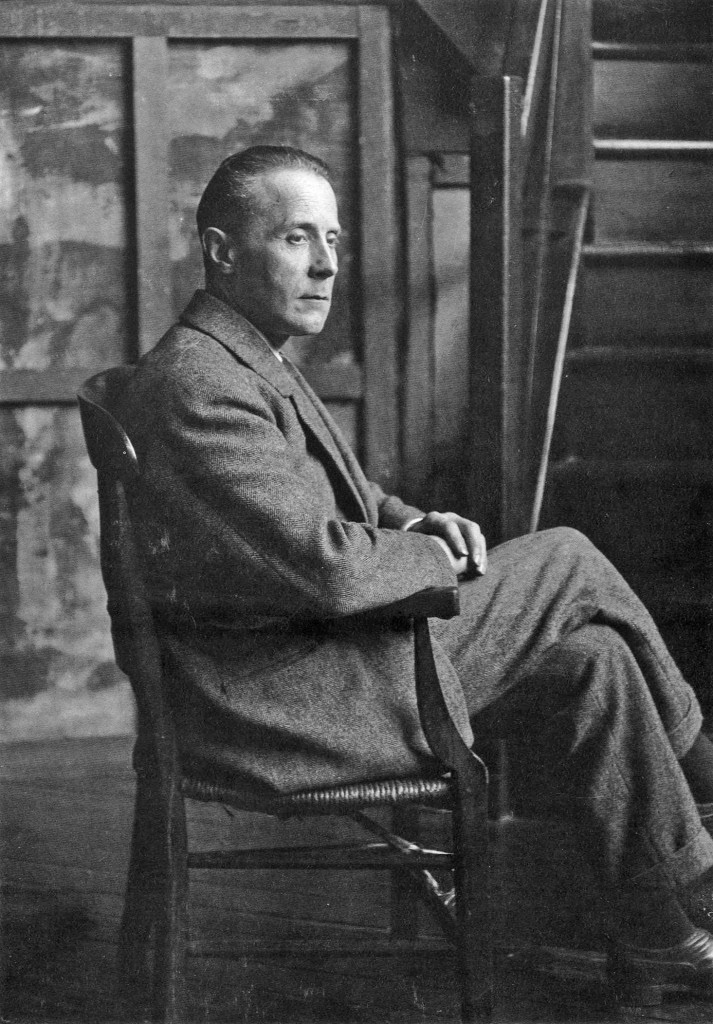

Jacques Villon, birth name Gaston Duchamp, was a French painter and printmaker. In 1907 he changed his name to Jacques Villon. He was the brother of artists Marcel Duchamp and Raymond Duchamp-Villon.
Villon began his career as a painter and his early work was influenced by the Impressionists and Post-Impressionists. He later became interested in Cubism and, together with his brother Raymond, became a member of the Putot group, a collective of artists who experimented with Cubist techniques.
In addition to painting, Villon was also a skilled engraver. He worked in various engraving techniques, including etching, aquatint and dry glass, and his prints are known for their intricate lines and geometric shapes.
Villon's work continued to evolve throughout his career, experimenting with different styles and techniques. In his later years, he returned to a more traditional style of painting, creating landscapes and portraits with bright colors and expressive strokes.
Villon's works were exhibited in major museums and galleries around the world, including the Museum of Modern Art in New York and the Pompidou Centre in Paris. He is considered to be one of the most significant figures of the Cubist movement and his contribution to modern art is still celebrated today.
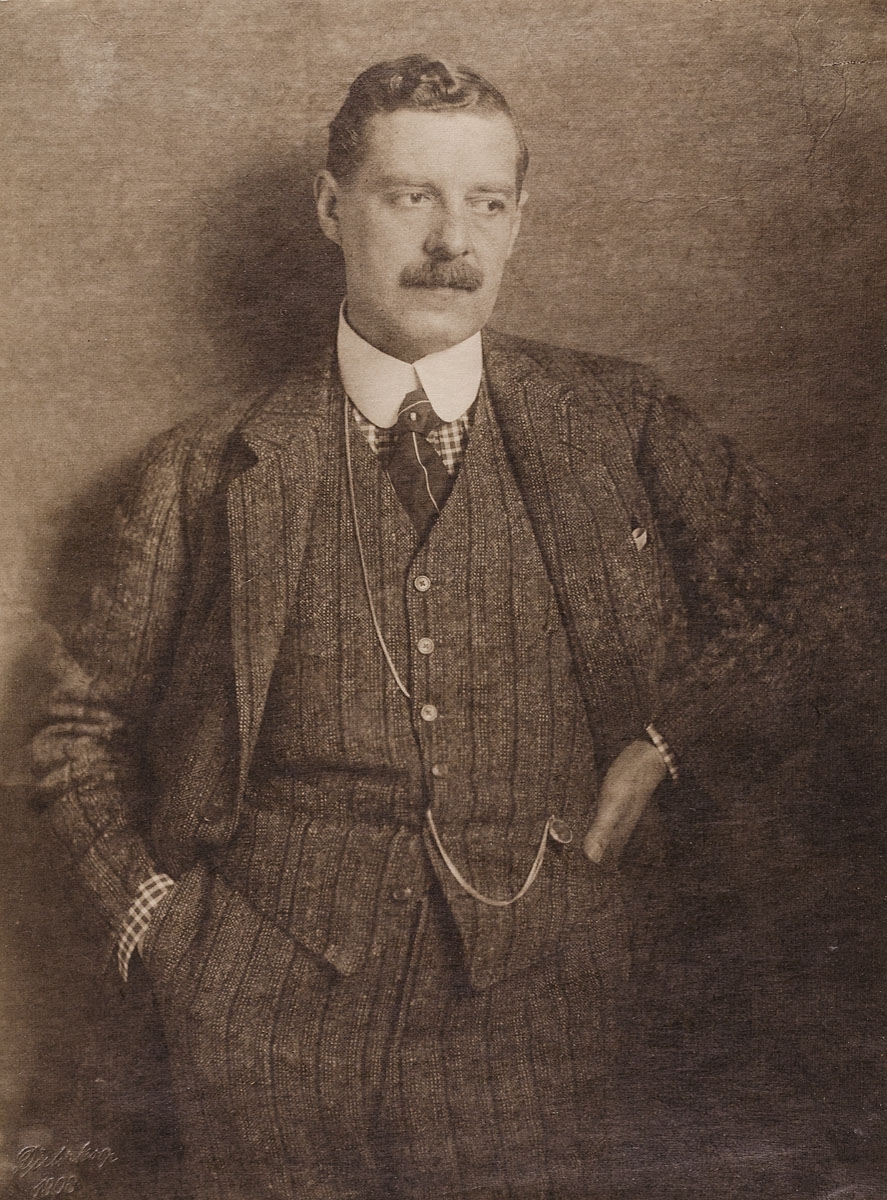


Peter Behrens was a seminal figure in modern design and architecture, heralded as the first industrial designer and a pioneer in modernist architecture. Born in Hamburg, Germany, Behrens's influence spanned across various domains, including architecture, industrial design, and graphic design. His holistic design approach was revolutionary, encompassing everything from architectural projects to corporate identities.
Behrens's association with AEG (Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft) marked a significant chapter in his career. Hired as an artistic consultant in 1907, he crafted a comprehensive corporate identity for AEG, including the iconic AEG Turbine Factory (1909), a hallmark of industrial classicism and modernism. This work is celebrated for its pioneering approach to industrial architecture and design, integrating form and function with unprecedented clarity and coherence.
His architectural ventures displayed a versatility and an evolution of style, from the monumental, stripped classical form seen in the German Embassy in St Petersburg (1912) and the Administration Building for Continental AG in Hannover (1912-1914), to the expressive Brick Expressionism of the Technical Administration Building of Hoechst AG in Frankfurt (1920-1924). Behrens's work in the 1920s, including the design for the 'New Ways' house in Northampton, UK, and contributions to the Weissenhof Estate in Stuttgart, underscored his shift towards New Objectivity and modernist principles.
Moreover, Behrens's educational contributions were profound, with his teaching stints at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna influencing a new generation of architects, including luminaries such as Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, Le Corbusier, and Walter Gropius, who would themselves go on to define the course of 20th-century architecture.
Behrens's legacy is a testament to the transformative power of design, illustrating how integrated and forward-thinking approaches can redefine our built environment and the objects we use daily. His work remains an essential study for collectors, experts in art and antiques, and anyone interested in the evolution of modern design and architecture.
For updates on exhibitions and auctions featuring Peter Behrens's work, sign up for our newsletter. Stay informed about new discoveries, sales, and events related to this pivotal figure in modern architecture and design.


Peter Behrens was a seminal figure in modern design and architecture, heralded as the first industrial designer and a pioneer in modernist architecture. Born in Hamburg, Germany, Behrens's influence spanned across various domains, including architecture, industrial design, and graphic design. His holistic design approach was revolutionary, encompassing everything from architectural projects to corporate identities.
Behrens's association with AEG (Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft) marked a significant chapter in his career. Hired as an artistic consultant in 1907, he crafted a comprehensive corporate identity for AEG, including the iconic AEG Turbine Factory (1909), a hallmark of industrial classicism and modernism. This work is celebrated for its pioneering approach to industrial architecture and design, integrating form and function with unprecedented clarity and coherence.
His architectural ventures displayed a versatility and an evolution of style, from the monumental, stripped classical form seen in the German Embassy in St Petersburg (1912) and the Administration Building for Continental AG in Hannover (1912-1914), to the expressive Brick Expressionism of the Technical Administration Building of Hoechst AG in Frankfurt (1920-1924). Behrens's work in the 1920s, including the design for the 'New Ways' house in Northampton, UK, and contributions to the Weissenhof Estate in Stuttgart, underscored his shift towards New Objectivity and modernist principles.
Moreover, Behrens's educational contributions were profound, with his teaching stints at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna influencing a new generation of architects, including luminaries such as Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, Le Corbusier, and Walter Gropius, who would themselves go on to define the course of 20th-century architecture.
Behrens's legacy is a testament to the transformative power of design, illustrating how integrated and forward-thinking approaches can redefine our built environment and the objects we use daily. His work remains an essential study for collectors, experts in art and antiques, and anyone interested in the evolution of modern design and architecture.
For updates on exhibitions and auctions featuring Peter Behrens's work, sign up for our newsletter. Stay informed about new discoveries, sales, and events related to this pivotal figure in modern architecture and design.